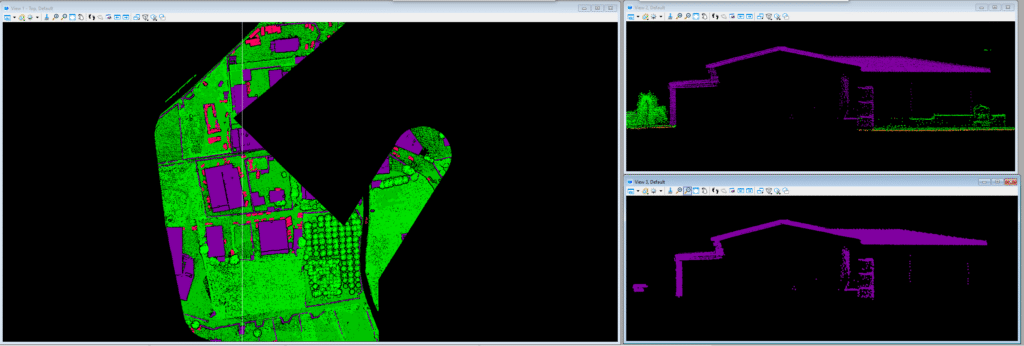
Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) is a remote sensing technology that uses laser light to measure the distance between an aircraft and the ground. This creates a high-resolution 3D point cloud of the terrain, which can be used to generate detailed topographic maps and 3D models.
Here’s a simplified overview of the ALS process:

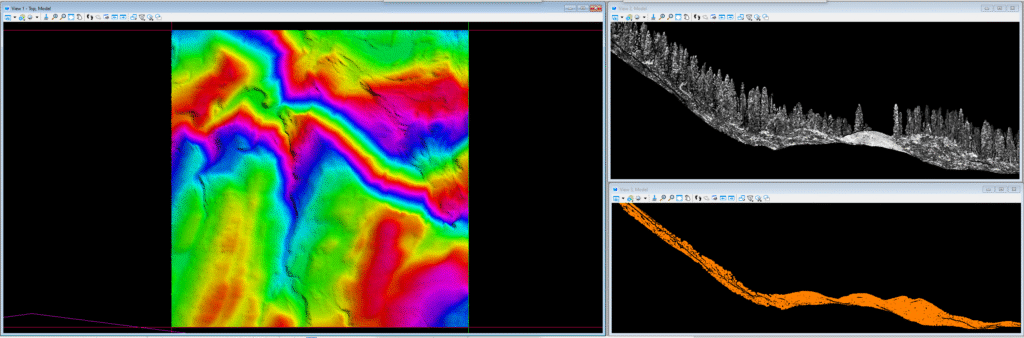
ALS has a wide range of applications, including:
ALS offers several benefits, including:

Ground classification
Hydro flattening
Advance classification
Power line classification
Volume calculation
DSM/ DTM/Contour